IP Telephony System Components
IP telephony uses modern technology to enable telephone calls to travel over "Internet Protocol" data networks. Here are some of the important components that make it work:
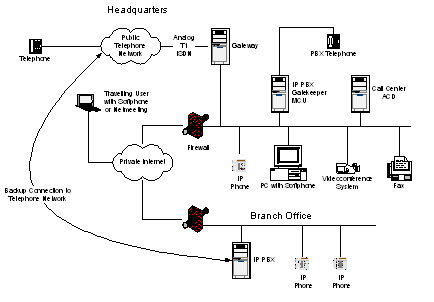
IP PBX
The IP PBX performs services for users such as call forwarding and voicemail. It also provides switchboard services and call routing, e.g. "Press 1 for Sales".
Gatekeeper
The gatekeeper is the "traffic cop" of an IP telephony system. It routes calls between the various endpoints in the system --phones, gateways, multi-conference units, etc. It controls who is allowed to use the system and when. It also manages how devices use the network, ensuring that time-critical voice traffic has priority while controlling total network usage and maintaining quality of service.
Gateways
Gateways seamlessly connect IP phones to other telephone systems, including the traditional public telephone network and legacy PBX systems.
Gateways can also be used to "IP enable" a legacy PBX, allowing calls to be routed over the IP data network instead of the telephone network, saving on call costs. This "least cost routing" also allows you to centralize your telephone resources, reducing administrative costs.
Multi-Conference Unit (MCU)
An MCU allows a large number of users to join a single audio or video conference simultaneously. It manages the conference, controlling who can get in and allowing a moderator to control the discussion. The MCU can transcode data streams, allowing systems using different communications protocols or network speeds to communicate
at the same time. It may also interface to a streaming video server when a conference or seminar will be recorded for later viewing on demand.
Automatic Call Director/Interactive Voice Response
Large volume applications such as call centers require sophisticated control over how calls are routed. An automatic call director (ACD) queues calls for agents, prioritizing and routing calls according to the caller and agent specialties. Interactive voice response (IVR) systems offer voice prompts and read information from users to tailor calls, often accessing databases during the call. IP telephony technology eases the development of sophisticated applications while reducing operating costs.
IP Telephone
An IP telephone works just like the traditional PBX phone that sits on your desk, it simply plugs into the network instead of the telephone line. IP phones make employee moves easy, as the phone number is associated with the phone not the physical line.
IP Softphone
A softphone is software that turns your PC into a virtual telephone. In addition to advanced calling features and directory services, it typically offers video calling. Softphones make advanced applications easy because they are based on IP technology. For example, you can simply click on a name in your address book to dial the phone number.